What Is Galvanizing and How Does It Work?
Have you noticed your metal equipment corroding? You may want to consider galvanizing. What is galvanizing, and how does it work? Find out in this article.

Once you’ve invested in quality iron or steel equipment, it’s important to maintain that equipment well. In addition to cleaning that equipment properly, it’s essential to protect it, and one way to do this is through galvanization. But what is galvanizing, and how does it work? This article will answer those questions.
What Is Galvanizing?
Galvanizing is the process of protecting a metal from corrosion using zinc. In the galvanization process, a zinc coating is added to the surface of the metal to prevent rusting. By reducing the corrosion of the metal on which the process is performed, galvanization increases the lifespan of the metal. There are several methods of galvanization; the most popular is hot-dip galvanization, but other methods are also common, including shepardizing, zinc-rich painting, and electroplating.
The Galvanizing Process
Hot-dip galvanizing is the most common kind of galvanizing. The process is fairly straightforward and involves just a few basic steps.
Surface Preparation
Before the galvanizing process begins, the surface of the metal must be prepared. Any excess materials, including paint, oil, and dirt, must be removed from the surface of the metal. This process is called degreasing. Next, the metal is pickled in an acid solution, usually hydrochloric acid, which removes any rust or scale that has accumulated on the surface of the metal. After each step, the metal must be rinsed with water.
Fluxing
After the surface of the metal has been cleaned and prepared, the metal is dipped in flux. This step serves to remove any oxidation that has formed on the surface of the metal during the degreasing and pickling steps.
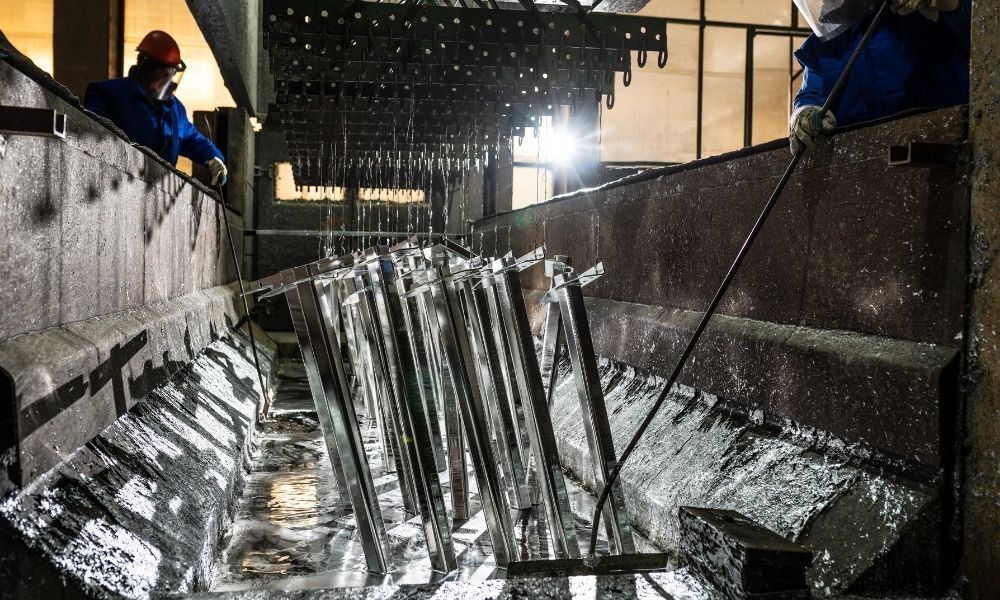
Galvanizing
Finally, the clean metal is immersed in molten zinc and galvanized. The zinc reacts with the metal to create protective zinc-alloy layers. After a period of time, the metal is removed from the zinc and is allowed to cool.
Post-Treatment
After the metal is galvanized, it is placed into a quench tank containing water and other chemicals that create another passivation layer to protect the metal. Finally, any excess zinc is removed from the surface of the metal, and the newly galvanized metal undergoes a final inspection.
Now that you understand what galvanizing is and how it works, you know why the galvanization process is so important. The galvanization process will extend the life of your metal equipment. But when it finally wears out, and you’re in the market for new equipment, be sure to choose a reliable custom metal manufacturer like CMPI.