Waterjet Cutting vs. Laser Cutting: A Comparison of Quality
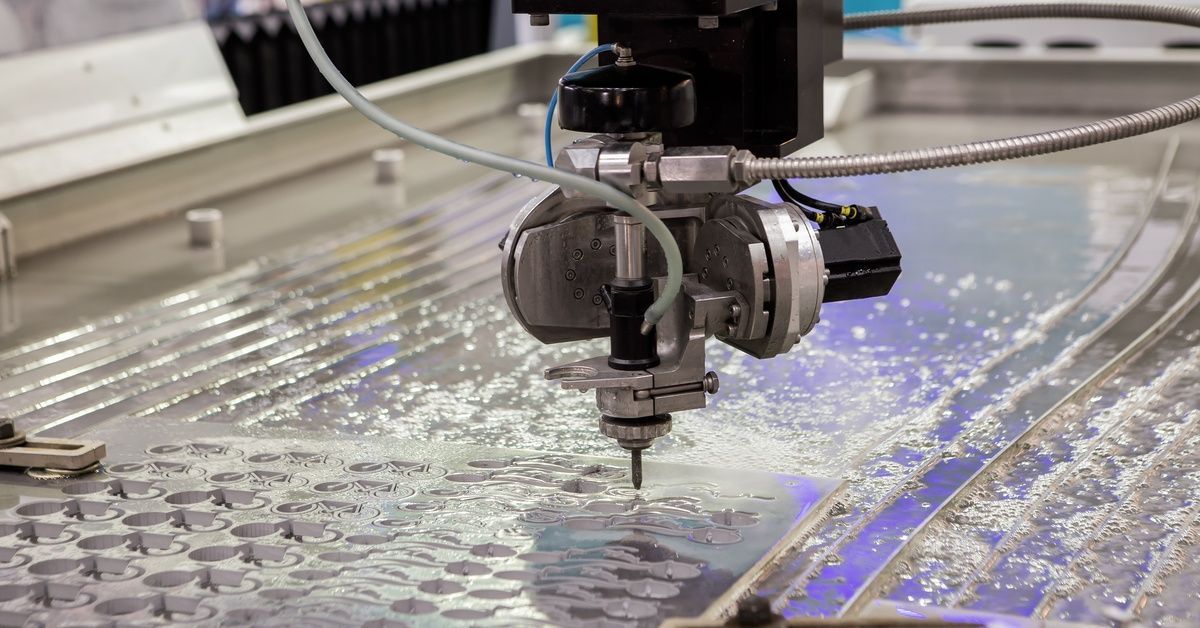

Manufacturing metal pieces requires precision, efficiency, and a commitment to producing exceptional results. The demand for quality is leading fabricators to focus on two prominent cutting technologies: waterjet and laser systems.
A comparison of quality between the technologies reveals that waterjet cutting systems excel with thick materials, while laser cutting systems offer rapid processing speeds and tight tolerances. The latter is ideal for high-volume production runs. Understanding these differences helps manufacturers make informed decisions for their requirements.
How the Technology Works
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive material to slice through materials. Because it does not use heat, waterjet cutting prevents thermal distortion and preserves the material’s integrity.
Laser cutting uses a concentrated beam of light to melt or vaporize the material. While the heat involved can create a narrow heat-affected zone, skilled operators control the process to minimize distortion.
Material Versatility
Waterjet technology cuts virtually any material, including metals, ceramics, glass, composites, and exotic alloys. The process handles materials up to 12 inches thick in some applications, opening possibilities for dense components.
Material options are more limited with laser cutting machines. This technology works well with metals—steel, aluminum, and stainless steel—with moderate thickness.
Speed and Efficiency Considerations
Production speed varies between these technologies. When manufacturers use laser cutting systems for thin materials, they achieve cutting speeds that dramatically outpace waterjet alternatives. This delivers a substantial productivity advantage in comparison to slower methods while maintaining quality standards.
Waterjet cutting requires more time per part but eliminates secondary operations like deburring or edge finishing. The complete edge preparation reduces downstream processing requirements while offsetting longer cutting times in total manufacturing cycles.
Cost Considerations
Operating costs differ between technologies. Waterjet systems consume significant amounts of abrasive material and high-pressure water, while laser systems require electrical power and periodic consumable replacement. Initial equipment investment varies based on power requirements and automation features.
Making the Right Choice
The right cutting technology changes with your materials and needs. Waterjet cutting is ideal for thick materials, alloys, or zero heat input. Laser cutting optimizes the production of thin to medium-thickness materials with an emphasis on speed and efficiency. Stainless steel fabrication service providers, like CMPI, utilize both systems to maximize capabilities across diverse customer requirements.