Exploring ASTM F3016 and F2656 Bollard Crash Standards
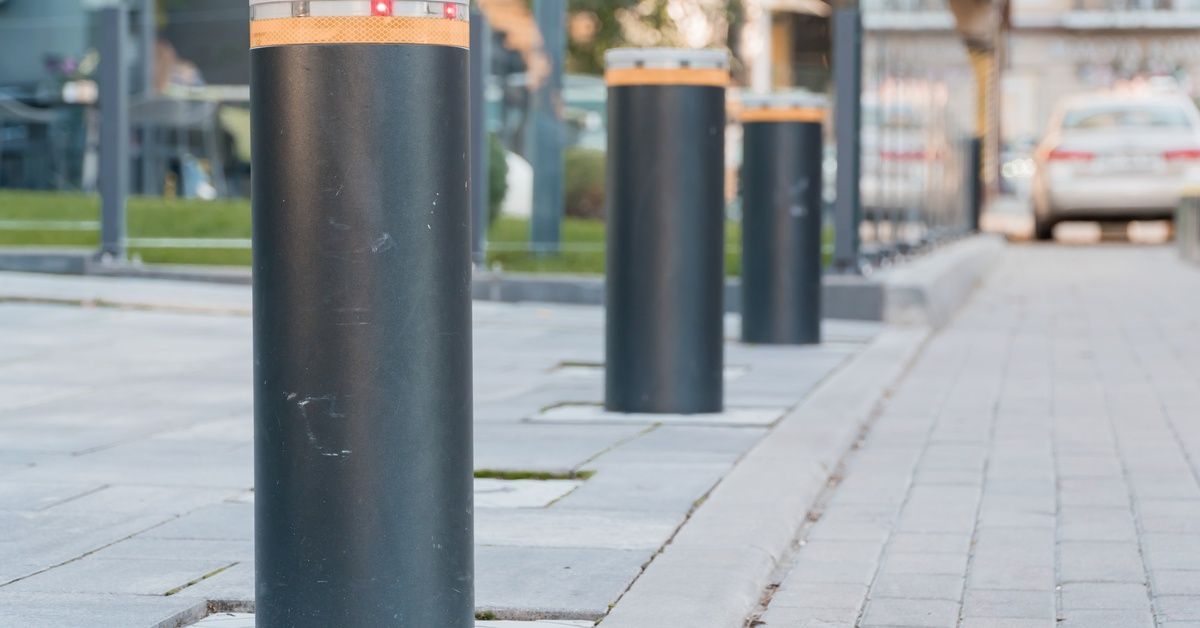

In high-traffic areas, many facility managers add bollards to protect buildings and pedestrians from potential vehicle impacts. Bollards are subject to strict testing protocols set by the American Society for Testing and Materials, specifically ASTM F3016 and ASTM F2656. Exploring ASTM F3016 and F2656 bollard crash standards helps you choose the right solutions for safety and compliance.
What Is ASTM F2656?
ASTM F2656 focuses on testing security barriers, including bollards, against vehicle impacts. The standard establishes specific test conditions using a 15,000-pound truck traveling at speeds ranging from 30 to 50 mph. The testing measures penetration distance—how far the vehicle travels beyond the barrier after impact—and determines the bollard’s effectiveness rating.
The classification system combines two ratings: a K rating for kinetic energy and a P rating for penetration distance. K4 represents 30 mph impacts, K8 indicates 40 mph, and K12 designates 50 mph. The P rating measures how far the vehicle travels beyond the barrier, with P1 being the highest performance level at 3.3 feet or less penetration. For example, a K12/P1 rating means the bollard stops a 50-mph truck impact with minimal penetration into the protected area.
What Is ASTM F3016?
While F2656 focuses on high-speed impacts, the ASTM F3016 standard was developed to address lower-speed threats. This standard specifically tests a bollard’s ability to stop a 5,000-pound vehicle (similar to a large SUV or pickup) at speeds of 10, 20, and 30 mph.
ASTM F3016 is particularly relevant for storefronts, sidewalks, and outdoor dining areas where accidental or low-speed intentional impacts are more common. An F3016 rating ensures that a bollard provides effective protection in these everyday settings.
Material Selection and Durability
A bollard’s material plays a significant role in its performance. Steel, particularly stainless steel, is a preferred choice for many installations. It provides high strength, corrosion resistance, and long-term durability. For commercial and municipal projects, working with reliable stainless steel bollard manufacturers ensures that the bollards meet crash standards and maintain their structural integrity over time.
Practical Considerations for Installation
To install bollards correctly, engineers must evaluate soil type, embedment depth, and spacing. Proper alignment and secure anchoring prevent failures that could compromise safety. Designers also need to consider accessibility and integration with existing structures. Attention to these details guarantees that bollards meet crash standards and function reliably in real-world conditions.
Selecting the Right Standard for Your Application
Security professionals must evaluate their specific threat scenarios when choosing between F2656 and F3016-rated bollards. High-security government facilities typically require F2656-rated barriers capable of stopping large trucks, while commercial properties might find F3016-rated bollards sufficient for their protection needs.
Exploring ASTM F3016 and F2656 bollard crash standards helps facility managers make informed decisions about perimeter security investments. The standards provide objective performance metrics that eliminate guesswork from bollard selection processes.