Heat Distortion Challenges in Stainless Steel Fabrication
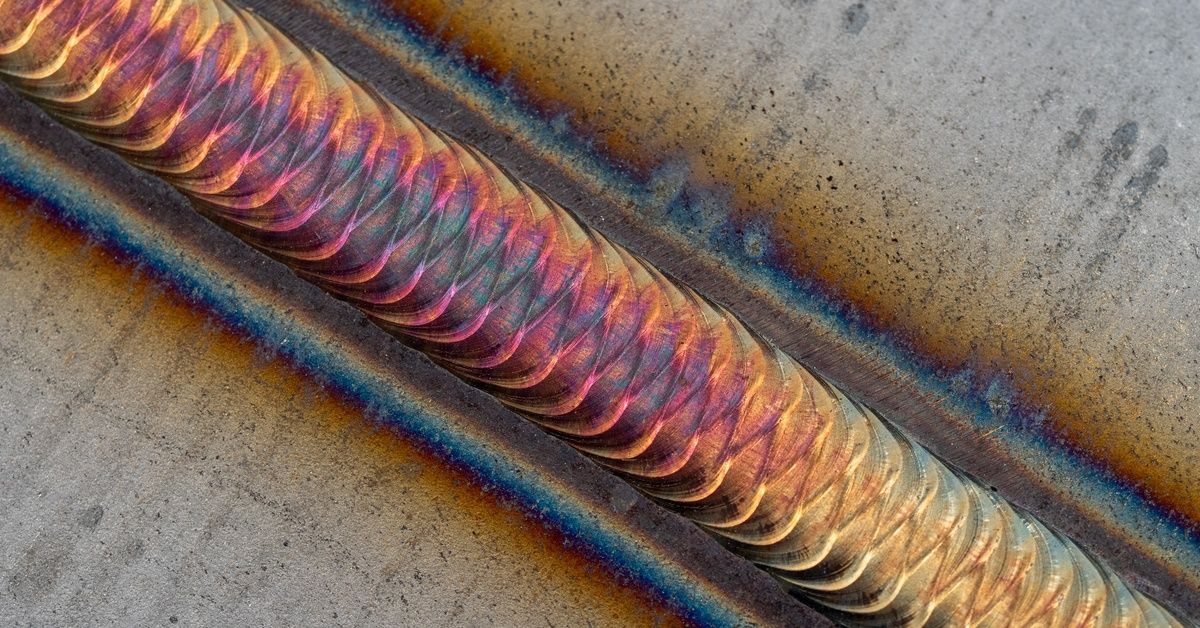

Stainless steel offers exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred material across many industries. However, its unique thermal properties present heat distortion challenges in stainless steel fabrication. Understanding and managing these properties is necessary for achieving the precision and structural integrity required in high-quality finished products.
The Role of Thermal Properties
Stainless steel possesses a high coefficient of thermal expansion and low thermal conductivity. This means the material expands when heated and does not dissipate that heat quickly. This combination creates localized hot spots during processes like welding, leading to uneven expansion and subsequent distortion as the metal cools and contracts.
These inherent material characteristics are the primary drivers of warping and buckling. Fabricators must carefully control heat input to manage these effects and maintain dimensional accuracy throughout the production cycle.
Common Types of Heat Distortion
Heat distortion manifests in several distinct ways during fabrication. For example, angular distortion occurs when the welded joint bends out of its intended plane. Longitudinal shrinkage causes the component to shorten along the length of the weld, potentially leading to misalignment of assembled parts.
Another frequent issue, especially with thinner gauges, is buckling. This happens when compressive stresses from thermal expansion exceed the material's structural stability, causing it to wave or ripple. Each type of distortion requires specific mitigation techniques to prevent it.
The Impact of Material Thickness
The thickness of the stainless steel sheet or plate directly influences its susceptibility to heat distortion. Thinner materials heat up and cool down much faster than thicker sections, making them more prone to warping. This rapid thermal cycle offers a smaller window for heat to distribute evenly.
Consequently, working with thin-gauge material requires extremely precise control over welding parameters. Fabricators use lower heat inputs and faster travel speeds to minimize the total energy absorbed by the workpiece, thereby reducing the risk of distortion.
Proven Mitigation Strategies
Experienced fabricators employ a range of strategies to counteract heat distortion. Proper clamping and fixturing allow them to physically restrain the material and prevent it from moving as it heats and cools. Using heat sinks, such as copper or aluminum backing bars, helps draw thermal energy away from the weld zone.
Additionally, a well-planned welding sequence can balance the thermal stresses introduced into a component. By strategically alternating weld locations, fabricators can prevent an accumulation of stress in one area.
Overcome Your Fabrication Challenges
Successfully navigating the heat distortion challenges in stainless steel fabrication demands a deep understanding of material science and process control. Partner with experts for components to meet exact specifications for both performance and appearance. Custom Manufacturing & Polishing combines decades of experience in custom stainless steel fabrication to deliver superior results. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and bring your design to life.